Mobile Inline Gateway: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Inline gateway for IOS = | |||
There are different integration modes available for our merchants: | There are different integration modes available for our merchants: | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
== Fast payment == | == Fast payment == | ||
In case of Fast payment the Barion SDK handles all the heavy lifting and the full payment flow is controlled by it. | |||
=== Payment flow === | === Payment flow === | ||
The participants in the process are: | The participants in the process are: | ||
* Merchant: The entity that sells goods or provides services to purchase. | * '''Merchant''': The entity that sells goods or provides services to purchase. | ||
* Payer: The customer who wants to buy said services or goods. | * '''Payer''': The customer who wants to buy said services or goods. | ||
* Merchant app: The mobile app of the merchant that is used for the payment | * '''Merchant app''': The mobile app of the merchant that is used for the payment | ||
* '''Barion SDK''': The SDK that provides the inline functionality | |||
* '''Merchants' backend''': The backend server of the merchant | |||
* '''Barion API''': The Barion API | |||
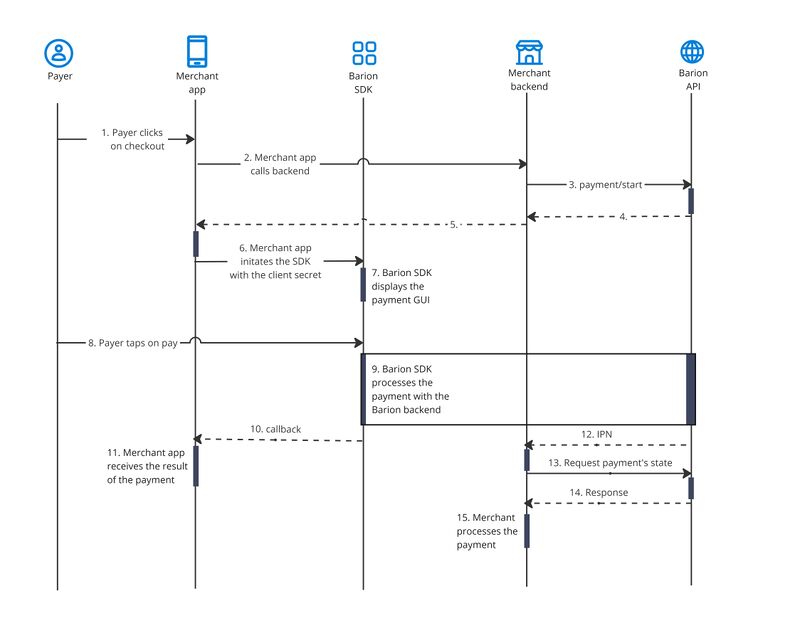
The payment process can be described in the following steps.[[File:IGW - Mobile flow PUBLIC.jpg|frameless|800x800px]] | The payment process can be described in the following steps. | ||
[[File:IGW - Mobile flow PUBLIC.jpg|frameless|800x800px]] | |||
'''1. Payer clicks on checkout''' | '''1. Payer clicks on checkout''' | ||
| Line 52: | Line 59: | ||
'''8. Customer inputs the card information or clicks on a wallet''' | '''8. Customer inputs the card information or clicks on a wallet''' | ||
'''9. Barion SDK forwards this to the Barion | '''9. Barion SDK forwards this to the Barion API''' | ||
The Barion system processes the payment. | |||
'''10. The Barion SDK calls back to the merchant's app code''' | '''10. The Barion SDK calls back to the merchant's app code''' | ||
This step is also described in the [https://github.com/barion/barion-ios Github library]. | |||
'''11. The merchant's app receives the result of the payment''' | '''11. The merchant's app receives the result of the payment''' | ||
From the callback the app receives the result of the payment. It is up to the merchant whether they trust this or query the result from the merchant's backend. The most secure way is to let the backend query the payment state and forward that information to the mobile app. | |||
'''12. Barion sends the instant payment notification request to the merchant's backend''' | '''12. Barion sends the instant payment notification request to the merchant's backend''' | ||
Revision as of 10:14, 20 January 2025
Inline gateway for IOS
There are different integration modes available for our merchants:
- Redirect/Hosted gateway: The merchants redirect the customer to secure.barion.com and the payer uses the GUI there to conduct the payment
- Inline gateway:
- Inline web gateway: The merchant displays the payment methods on its website seamlessly like it was created by the merchant.
- Inline mobile gateway: The merchant displays the payment methods in its mobile app seamlessly like it was created by the merchant.
This page describes the integration for the inline mobile gateway.
There are two ways to integrate the Barion Smart Gateway into a mobile app:
- Inline fast payment: The whole UI is displayed by the Barion SDK and the process is controlled inside the SDK.
- Inline elements: The SDK provides UI elements and the merchant has total freedom to place them on their checkout screen and process.
Fast payment
In case of Fast payment the Barion SDK handles all the heavy lifting and the full payment flow is controlled by it.
Payment flow
The participants in the process are:
- Merchant: The entity that sells goods or provides services to purchase.
- Payer: The customer who wants to buy said services or goods.
- Merchant app: The mobile app of the merchant that is used for the payment
- Barion SDK: The SDK that provides the inline functionality
- Merchants' backend: The backend server of the merchant
- Barion API: The Barion API
The payment process can be described in the following steps.
1. Payer clicks on checkout
The payer uses the merchant's mobile app to start the checkout.
2. Merchant app calls the merchant backend
This is necessary since only the backend can be trusted to communicate securely with the Barion API.
3. The merchant's backend calls the Barion API
The merchant's backend call the payment/start endpoint. In case there is already a Barion Smart Gateway integration in place, the merchant does not have to add any new information to the request.
4. Receives back a secret in the response
There is an additional property in the response, called ClientSecret. This is used to initiate the Barion inline SDK.
5. The merchant’s backend forwards the secret to the merchant’s mobile app
The merchant's backend needs to forward the ClientSecret to the merchant's mobile app.
6. Merchant's app initializes the Barion SDK
The merchant's mobile app initializes the Barion SDK. The detailed description of this step is written up in the Github library.
7. The Barion SDK displays the payment options
8. Customer inputs the card information or clicks on a wallet
9. Barion SDK forwards this to the Barion API
The Barion system processes the payment.
10. The Barion SDK calls back to the merchant's app code
This step is also described in the Github library.
11. The merchant's app receives the result of the payment
From the callback the app receives the result of the payment. It is up to the merchant whether they trust this or query the result from the merchant's backend. The most secure way is to let the backend query the payment state and forward that information to the mobile app.
12. Barion sends the instant payment notification request to the merchant's backend
13. The merchant's backend request the state of the payment
14. The payment state response contains the result of the process
15. The merchant processes the order