C2C Payments: Difference between revisions
m (Birot moved page Sharing economy payments to C2C Payments without leaving a redirect) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==C2C overview== | ==C2C overview== | ||
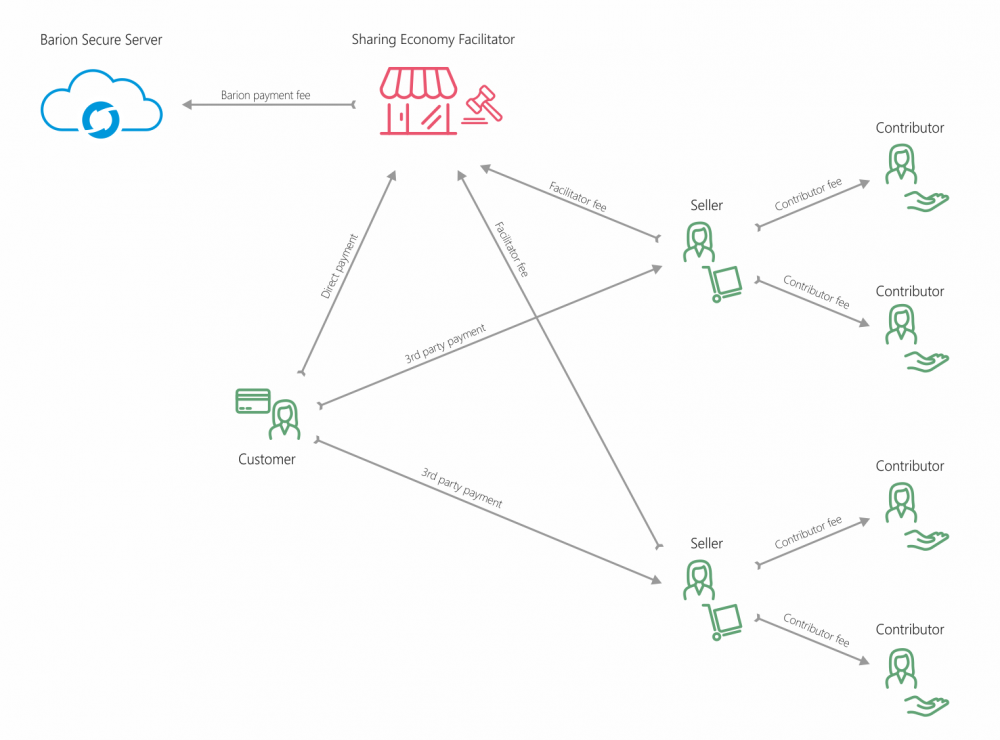
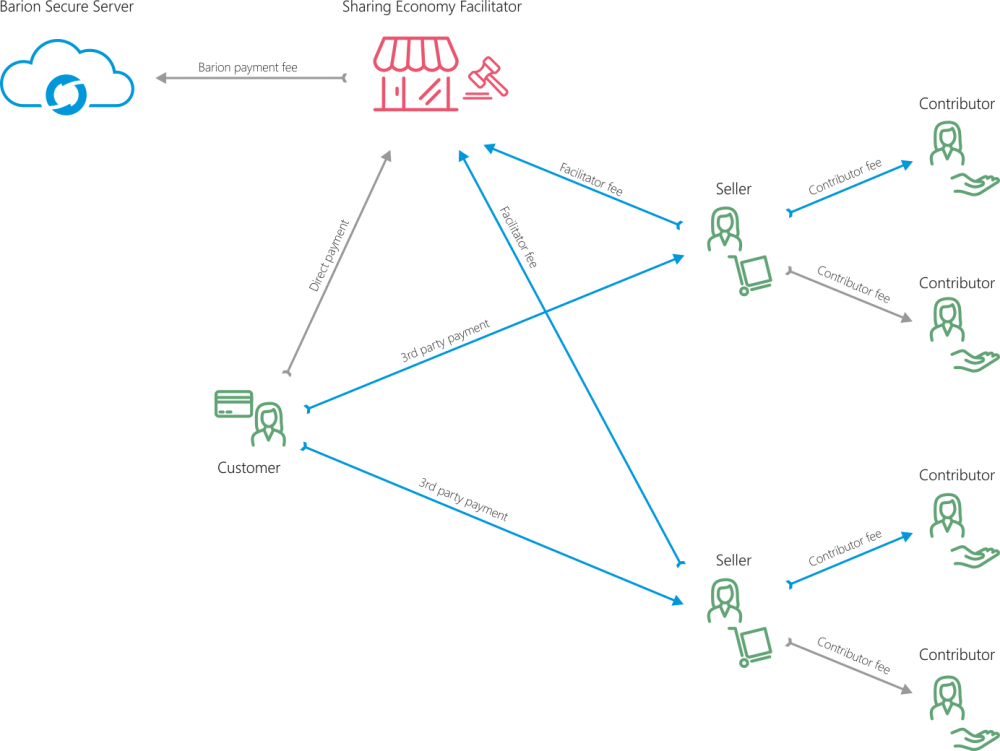
In certain business scenarios Barion is able to facilitate payments between users of the system. Hence the name C2C, meaning consumer to consumer. There are roles, as indicated on the diagram. The Customer is the user who uses the services of Seller (or multiple Sellers in case of marketplaces) and pays the Seller directly. The Facilitator, the company that facilitates the service is organizing the payment with the Barion API. The Facilitator is able to transfer a fee from each payment to herself and to one or more Contributors. The Customer does not need a Barion account, but the Seller and Contributors do. Barion transaction fees are always covered by the Facilitator, no other parties pay transaction fees. | In certain business scenarios Barion is able to facilitate payments between users of the system. Hence the name C2C, meaning consumer to consumer. There are roles, as indicated on the diagram. The Customer is the user who uses the services of Seller (or multiple Sellers in case of marketplaces) and pays the Seller directly. The Facilitator, the company that facilitates the service is organizing the payment with the Barion API. The Facilitator is able to transfer a fee from each payment to herself and to one or more Contributors. The Customer does not need a Barion account, but the Seller and Contributors do. Barion transaction fees are always covered by the Facilitator, no other parties pay transaction fees. | ||
[CodeSamples|Code Samples] are available. | |||
Examples of use for such payments: | Examples of use for such payments: | ||
Revision as of 15:31, 4 September 2017
C2C payments - sharing economy and marketplaces
C2C overview
In certain business scenarios Barion is able to facilitate payments between users of the system. Hence the name C2C, meaning consumer to consumer. There are roles, as indicated on the diagram. The Customer is the user who uses the services of Seller (or multiple Sellers in case of marketplaces) and pays the Seller directly. The Facilitator, the company that facilitates the service is organizing the payment with the Barion API. The Facilitator is able to transfer a fee from each payment to herself and to one or more Contributors. The Customer does not need a Barion account, but the Seller and Contributors do. Barion transaction fees are always covered by the Facilitator, no other parties pay transaction fees.
[CodeSamples|Code Samples] are available.
Examples of use for such payments:
- Sharing Economy business model (such as Uber)
- Marketplaces, where shopper may buy from multiple Sellers in one transaction
- Where law mandates direct payment to Seller, e.g. in certain insurance scenarios
- To optimize taxation
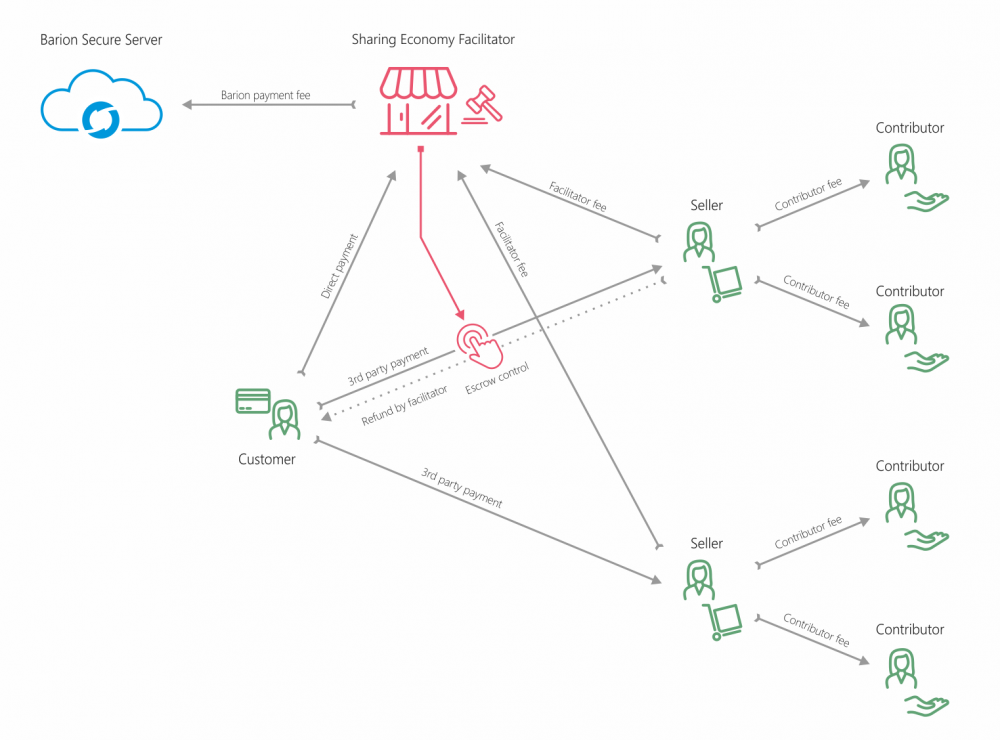
C2C with escrow
The Facilitator has the option to control the payment of the Customer to Seller, by placing the sum in an escrow and decide about fulfillment at a later time, such as when the delivery is confirmed. The funds can be partially or completely refunded to the Customer in case Seller does not deliver properly.
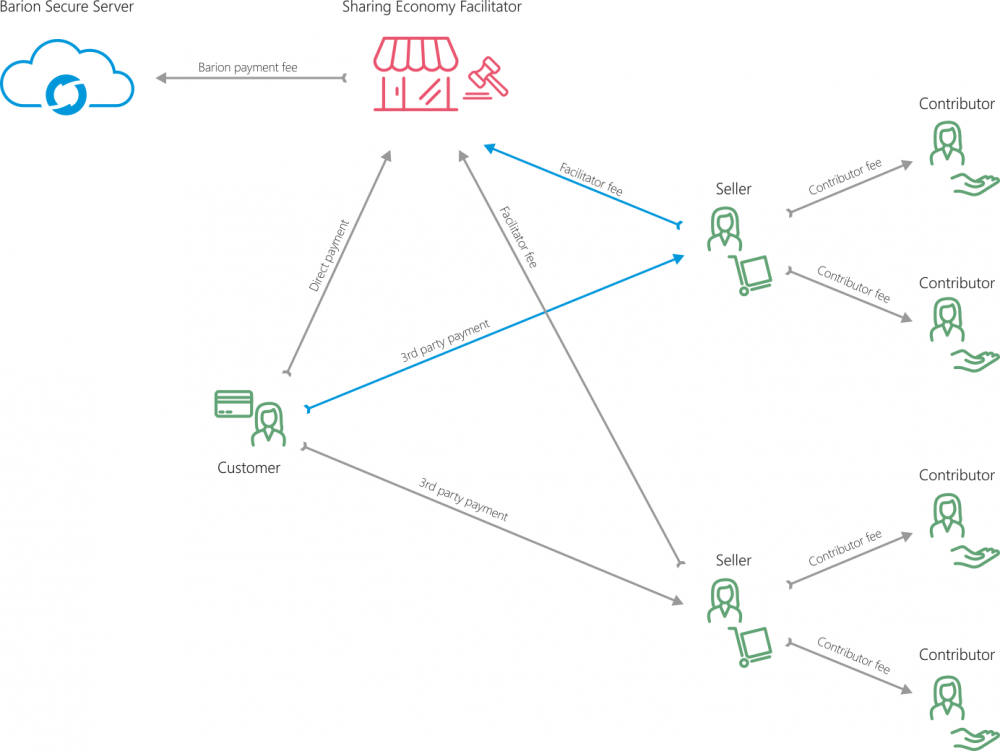
"Uber" style simple sharing economy example
If "Uber" was using Barion, the passenger would be the Customer, and the Driver would be the Seller. "Uber" would ask for a fee from the driver, as the blue lines indicate. Barion transaction fees would be payed by "Uber". Drivers would need a Barion account set up before the first ride. Automatic charging would be solved by Token payments.
"Marketplace with agents" sharing economy example
This example shows a marketplace, where multiple Sellers sell goods or services to the Customer, and both the Facilitator and third party agents receive a fee.
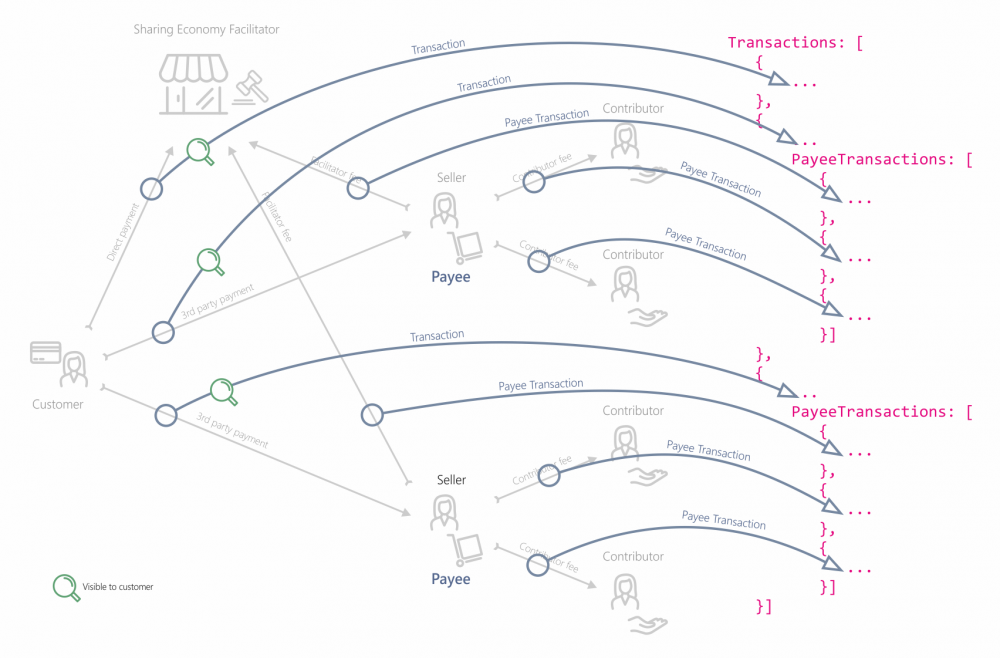
C2C transactions mapped to API structure
The following diagram helps developers match the C2C payment structure the the API Json structure.