Calling the API: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (→Authentication) |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
== Authentication == | == Authentication == | ||
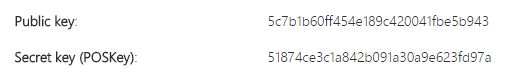
For every request sent to the Barion API you have to authenticate yourself. For this every API request should cointain a <code>POSKey</code> property containing the secret API key for the shop. This key is in the confirmation e-mail that was sent to you when you opened the shop or can be copied from the details page of the shop (secure.barion.com -> Manage my shops -> Details). This is unique for every shop in the system. Be aware that the test and live environment are completely separate environments, you need to create different shops. Make sure that you use the | For every request sent to the Barion API you have to authenticate yourself. For this every API request should cointain a <code>POSKey</code> property containing the secret API key for the shop. This key is in the confirmation e-mail that was sent to you when you opened the shop or can be copied from the details page of the shop (secure.barion.com -> Manage my shops -> Details). This is unique for every shop in the system. Be aware that the test and live environment are completely separate environments, you need to create different shops. Make sure that you use the POSkey and not the public key: | ||
[[File:Poskey.jpg]] | [[File:Poskey.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 08:50, 12 March 2019
Calling the Barion API
The Barion API
Barion offers you a RESTful API service to communicate with your web or mobile merchant services. Learn more about RESTful behavior the original Wikipedia article.
Protocols and communication
The Barion API communicates via standard HTTP1.1 GET or POST requests. A given API endpoint accepts only GET or only POST requests - there are no universal endpoints available. On each API endpoint reference page, you can find the path of the API endpoint and the HTTP method it accepts.
Example:
| POST | /v2/Payment/Start |
|---|
If the caller uses an incorrect method, the system responds with a JSON error message.
Example: calling a POST endpoint with a GET request
{
"Message": "The requested resource does not support http method 'GET'."
}Data and content types
The API sends and receives all content in standard JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) string format.
Some things you must ensure when creating an API request:
- JSON strings are UTF-8 encoded.
- The MIME type of the request sent to the API is defined as
application/json. Content-lengthshould also be specified explicitly in all HTTP request headers.
The data types used in the API communication are the following:
| Data type | Type description |
|---|---|
| string | Standard character string. The Barion API uses UTF-8 encoding. |
| int | 32-bit signed integer format |
| GUID (Global Unique Identifier) | A 128-bit long hexadecimal identifier with 32 character string representation, like this: 21EC2020-3AEA-4069-A2DD-08002B30309D. Its value is always unique in the Barion system. This is used e.g. to identify payments. |
| DateTime | Date and time values, represented in a string format of the ISO-8601 standard, like this: 2014-12-06T08:35:46Z. All API call responses contain datetimes as strings. |
| TimeSpan | A time range value represented in a string format of the ISO-8601 standard, like this: 3.14:15:28 (three days, fourteen hours, fifteen minutes, twenty-eight seconds). All API call responses contain datetimes as strings. |
| bool | Boolean true or false values.
Note: avoid integer or byte evaluation when constructing the request JSON! |
| byte | Byte representation of an enumeration value. This is only for internal use in the Barion system, API call responses always contain the string representation. |
API URLs
The base URL for the Barion API depends on the environment you are connecting to.
Base URL for API requests in the Live (production) environment: https://api.barion.com
Base URL for API requests in the Sandbox (test) environment: https://api.test.barion.com (learn more about the Sandbox environment here)
Note: Always double check that you are connecting to the proper environment to avoid unnecessary hassle and troubleshooting!
API versioning
To avoid breaking changes, whenever there is a major update to an API endpoint, it is moved to a higher level of API version. At the moment, the Barion API offers two different API versions (noted v1 and v2). Some API endpoints are only available in v1 or v2. See the reference page of a given API endpoint to see which versions are available.
Note: Though version numbers can be omitted from the endpoint path (such requests always fall back to v1), it is recommended to always specify the API version when sending requests to the Barion API to avoid confusion.
Example paths:
https://api.barion.com/Transaction/List- implicit call to av1endpoint (version number is omitted from path)https://api.barion.com/v1/Transfer/Send- explicit call to av1endpointhttps://api.barion.com/v2/Payment/Start- explicit call to av2endpoint
Authentication
For every request sent to the Barion API you have to authenticate yourself. For this every API request should cointain a POSKey property containing the secret API key for the shop. This key is in the confirmation e-mail that was sent to you when you opened the shop or can be copied from the details page of the shop (secure.barion.com -> Manage my shops -> Details). This is unique for every shop in the system. Be aware that the test and live environment are completely separate environments, you need to create different shops. Make sure that you use the POSkey and not the public key:
If the key is invalid you will receive an AuthenticationFailed error.
Handling the response
The structure of the response varies from endpoint to endpoint however on property can found in all of them. Every API response contains an Errors array. If this array is empty then the request was processed successfully. This array can contain multiple errors so make sure that the integration is prepared for this. The errors have the following fields>
| FieldName | Description |
|---|---|
| ErrorCode | The error code of the payment, this can be interpreted as an error Id. |
| Title | The title of the error, this is a more readable form of the error. |
| Description | The description of the error, more information about the error. |
| EndPoint | The URL of the API endpoint to help the reproduction of the error scenario. |
| AuthData | The e-mail address of the caller to help the reproduction of the error scenario. |
| HappenedAt | The timestamp of the response. |
Example error response
{
"Errors": [
{
"ErrorCode": "NotExistingPaymentId",
"Title": "The given payment id is invalid",
"Description": "The given payment id(510bbd38-08c9-40b9-9e21-c6f6cb9eb4f1) is invalid!",
"EndPoint": "https://api.barion.com/v2/Payment/GetPaymentState?POSKey=5b65f8f7a5f4405bb19495383dcf170a&PaymentId=510bbd3808c940b99e21c6f6cb9eb4f1",
"AuthData": "[email protected]",
"HappenedAt": "2017-02-06T09:48:13.7694921Z"
}
]
}Security
Please refer to the Security Measures page for more information on IT security before staring to code.